There are a number of processes and procedures for maintaining and administering the Search Enterprise environment.
Pre-indexing considerations
The Exact Term search feature that allows searching using the equals operator =, is disabled by default to save index space.
It’s possible to enable it for specific properties and property types using the /alfresco/search/elasticsearch/config/exactTermSearch.properties configuration file located in the Alfresco Repository.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| alfresco.cross.locale.datatype.0 | A new cross locale field is added for any property of this data-type to enable exact term search. For example, {http://www.alfresco.org/model/dictionary/1.0}text. The Exact Term search is disabled by default. |
| alfresco.cross.locale.property.0 | A new cross locale field is added for the property to enable exact term search. For example, {http://www.alfresco.org/model/content/1.0}content. The Exact Term search is disabled by default. |
You can add as many data types and properties as you like by adding lines and incrementing the associated index:
alfresco.cross.locale.datatype.0={http://www.alfresco.org/model/dictionary/1.0}text
alfresco.cross.locale.datatype.1={http://www.alfresco.org/model/dictionary/1.0}content
alfresco.cross.locale.datatype.2={http://www.alfresco.org/model/dictionary/1.0}mltext
alfresco.cross.locale.property.0={http://www.alfresco.org/model/content/1.0}content
To overwrite this configuration when using Docker compose you can mount this file as an external volume. The following sample describes a local configuration to be applied to the Elasticsearch Search Subsystem when using Docker compose:
services:
alfresco:
volumes:
- ./exactTermSearch.properties:/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/alfresco/WEB-INF/classes/alfresco/search/elasticsearch/config/exactTermSearch.properties
Note: Once complete you must perform a re-index. It is recommended you enable the exact term feature before you start creating an index.
Alfresco Elasticsearch connector
Indexing is provided by a Spring boot application called the Elasticsearch connector. This application contains two main components that build and maintain the index in Elasticsearch.
-
Live Indexing: Metadata, and Content and Permissions from Alfresco Repository are consumed using ActiveMQ messages so they can be indexed in the Elasticsearch server. The information created and updated in the Alfresco Repository is not immediately available in Elasticsearch, because it takes time to process the messages coming from the Alfresco Repository. The previous Eventual consistency approach, based on transactions and used for Solr deployments, has been replaced by this new approach based on ActiveMQ messages.
-
Re-indexing: Indexing the information of a pre-populated Alfresco Repository or catching up with Alfresco Repositories that have missed some ActiveMQ messages is provided by the re-indexing component. Metadata and Permissions from the Alfresco Repository is retrieved using a direct JDBC connection to the Alfresco Database. Note: Only PostgreSQL is supported. The re-indexing application also generates content indexing messages in ActiveMQ in order to get the content indexed. It may take some time to process all these requests after the re-indexing application has finished.
New Repository
When creating a new Alfresco Repository you must use the Elasticsearch connector applications in the following sequence:
- Start the Content Services Stack, including the Elasticsearch connector live indexing services, and the Elasticsearch server.
- Configure the Elasticsearch connector re-indexing app to point to the database, the Elasticsearch server, and the ActiveMQ server.
- Run the re-indexing app from the command line replacing the connection details as appropriate:
$ java -jar alfresco-elasticsearch-reindexing-3.1.0-app.jar \
--alfresco.reindex.jobName=reindexByIds \
--spring.elasticsearch.rest.uris=http://localhost:9200 \
--spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/alfresco \
--spring.datasource.username=alfresco \
--spring.datasource.password=alfresco \
--spring.activemq.broker-url=tcp://localhost:61616?jms.useAsyncSend=true \
--alfresco.reindex.prefixes-file=file:reindex.prefixes-file.json
When completed successfully you will see:
o.s.batch.core.step.AbstractStep : Step: [reindexByIdsStep] executed in 4s952ms
o.a.r.w.ElasticsearchRepoEventItemWriter : Total indexed documents:: 845
o.a.r.listeners.JobLifecycleListener : Current Status: COMPLETED
Once the command has completed, metadata and permissions from the out-of-the-box repository nodes are indexed in the Elasticsearch server. Additionally, the Elasticsearch connector live indexer will add existing content, the new metadata, permissions, and new content when nodes are created, updated or deleted.
Existing Repository
When using a pre-populated Alfresco Repository, use the Elasticsearch connector applications in the following sequence:
- Ensure the Content Services Stack with SOLR, which is configured as the search subsystem, is running.
- Start the Elasticsearch server.
- Configure the Elasticsearch connector re-indexing app to point to the database, the Elasticsearch server, and the ActiveMQ server.
- Run the re-indexing app and replace the connection details as appropriate:
$ java -jar alfresco-elasticsearch-reindexing-3.1.0-app.jar \
--alfresco.reindex.jobName=reindexByIds \
--spring.elasticsearch.rest.uris=http://localhost:9200 \
--spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/alfresco \
--spring.datasource.username=alfresco \
--spring.datasource.password=alfresco \
--spring.activemq.broker-url=tcp://localhost:61616?jms.useAsyncSend=true \
--alfresco.reindex.prefixes-file=file:reindex.prefixes-file.json
When completed successfully you will see:
o.a.r.w.ElasticsearchRepoEventItemWriter : Total indexed documents:: 80845
o.a.r.listeners.JobLifecycleListener : Current Status: COMPLETED
Once the command has completed, metadata from any existing Repository nodes will be indexed in the Elasticsearch server. Additionally, the Elasticsearch connector live indexer will add existing content, which may take a while. Ensure ActiveMQ is available until all the content transformation request messages have been processed. Then change the Alfresco Repository configuration to use the Elasticsearch as the search subsystem and then re-start the Repository.
Note: To ensure all the content transformation requests have been processed the ActiveMQ Web Console should be used. By default, the Web Console is available at
http://127.0.0.1:8161and accessed using default credentials. Any queues related to content transformation, usually throughacs-repo-transform-request, should not have any pending messages.
Partial Indexing
Over time some data may not be indexed correctly. This can be caused by prolonged network connectivity issues. The re-indexing application provides two strategies to fill the gaps in the Elasticsearch index:
- Fetch by IDS (
alfresco.reindex.jobName=reindexByIds): index nodes in an interval of databaseALF_NODE.idcolumn. - Fetch by DATE (
alfresco.reindex.jobName=reindexByDate): index nodes in an interval of databaseALF_TRANSACTION.commit_time_mscolumn.
Ids Range
The following sample re-indexes all the nodes in the Alfresco Repository which have an ALF_NODE.id value between 1 and 10000.
java -jar target/alfresco-elasticsearch-reindexing-3.1.0-app.jar \
--alfresco.reindex.jobName=reindexByIds \
--alfresco.reindex.pagesize=100 \
--alfresco.reindex.batchSize=100 \
--alfresco.reindex.fromId=1 \
--alfresco.reindex.toId=10000 \
--alfresco.reindex.concurrentProcessors=2
Date Range
The following sample re-indexes all the nodes in the Alfresco Repository which have a value for ALF_TRANSACTION.commit_time_ms between 202001010000 and 202104180000. Date time values are written in the format yyyyMMddHHmm.
java -jar target/alfresco-elasticsearch-reindexing-3.1.0-app.jar \
--alfresco.reindex.jobName=reindexByDate \
--alfresco.reindex.pagesize=100 \
--alfresco.reindex.batchSize=100 \
--alfresco.reindex.concurrentProcessors=6 \
--alfresco.reindex.fromTime=202001010000 \
--alfresco.reindex.toTime=202104180000
Deploying at Scale
This section describes how to run Search Enterprise at scale. Recommendations are based on testing carried out against a 50 million node repository.
The following services are required:
- Alfresco Content Repository deployed as a Tomcat server using the
alfresco.warapplication. - Alfresco Database to store metadata and other relevant information for the content repository.
- Alfresco Transform Service deployed as a Spring boot application with several transformation services (ImageMagick, LibreOffice, PDF Renderer and LibreOffice).
- Alfresco Shared File store deployed as a Spring boot application to serve transformed files by the Transform Service.
- Alfresco Elasticsearch Connector deployed as a Spring boot application with several indexing services, mediation, metadata, and content.
- Alfresco ActiveMQ which is message-oriented middleware and shares messages between the content repository, the Elasticsearch connector and the Transform Service.
- Elasticsearch server.
Identifying critical paths
To identify the services used for the different features provided by Search Enterprise the following critical paths should be reviewed:
- Indexing metadata and permissions
- Indexing content
- Searching metadata and content
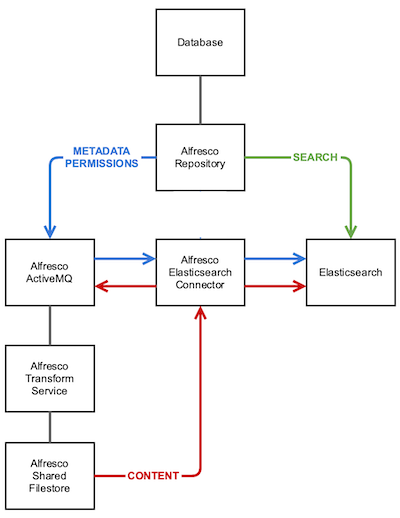
Metadata and Permissions
Each time a node is created or updated in the content repository, new messages with metadata and permissions are sent to ActiveMQ. The Elasticsearch connector consumes these messages and sends the indexing requests to the Elasticsearch server.
Content
Every time a content node is created or updated in the content repository, new messages are sent to ActiveMQ. The Elasticsearch connector consumes these messages from ActiveMQ and creates new transformation messages back into ActiveMQ. The Content Repository consumes the transformation messages and offloads the transformation of documents into plain text to the Transform Service. Once the transformation has been performed, the content repository produces a transformation complete message in ActiveMQ and uploads the plain text file to a Shared File store. The Elasticsearch connector consumes these messages and downloads the extracted text from the Shared File store. Then the text in the document is sent for indexing to the Elasticsearch server.
Searching metadata and content
Searching operations are handled by the content repository REST API. Depending on the search syntax used (only AFTS is currently supported), the content repository translates the search query to the Elasticsearch REST API language and sends the search request to Elasticsearch.
Metadata indexing performance
A misconfigured or deployed system can result in a significant delay between the time when documents are created or updated in the content repository and when they appear in the search results (indexed in the Elasticsearch server).
The following information describes how to identify bottlenecks in the system’s performance. It also gives recommendations on how to mitigate those bottlenecks when only indexing metadata.
Alfresco Repository
When the content repository is updating the database the document’s metadata in the database sends messages to the ActiveMQ topic alfresco.repo.event2. The rate of created or updated documents depends on the content repository cluster performance.
Recommendations:
- Increase resources for the server if CPU load or memory consumption is high.
- Increase database pool if no connections are available.
- Increase the number of threads if no threads are available.
- Increase the number of content repository nodes in the cluster.
Database
The database is updated to create new nodes or to modify existing ones. Additionally, the queries are executed in the database to populate metadata for returned entities in the REST API responses for search queries. These operations are mainly related to ALF_NODE and ALF_NODE_PROPERTIES tables.
Recommendations:
- Increase resources for the server if CPU load or memory consumption is high.
- Regularly update statistics for
ALF_NODEandALF_NODE_PROPERTIEStables to optimise query planner performance.
Elasticsearch connector
This service consumes messages from the ActiveMQ topic alfresco.repo.event2 and produces or consumes ActiveMQ messages from the queue metadata.event.
Recommendations:
- Always use a pool of connections to ActiveMQ (
spring.activemq.pool.enabledset totruewithspring.activemq.pool.max-connectionssized). - Increase the number of consumers for the
live-indexing-mediationcomponent if the messages enqueued count is significantly greater than messages dequeued for the ActiveMQ topicalfresco.repo.event2. - Increase the number of consumers for the
live-indexing-metadatacomponent if the messages enqueued count is significantly greater than messages dequeued for the ActiveMQ queuemetadata.event.
ActiveMQ
ActiveMQ transports messages from the content repository and the Elasticsearch connector. It also communicates between the content repository and the Transform Service communication.
Recommendations:
- Increase resources for the server if CPU load or memory consumption is high.
Elasticsearch server
The Elasticsearch server gets indexing requests from the Elasticsearch connector. If all other services are working as expected, an increment in messages enqueued without the dequeuing operation for queue metadata.event may indicate the Elasticsearch server requires more resources. Slow responses for a search query can also indicate insufficient resources for the server.
Recommendations:
- Increase resources for the server if CPU load or memory consumption is high.
- Increase resources for the server if ingestion rate is decreasing with higher volumes of data.
Permissions indexing performance
Alfresco Repository
Recommendations:
- Increase resources for the server if CPU load or memory consumption is high.
- Increase database pool if no connections are available.
- Increase the number of threads if no threads are available.
- Increase the number of content repository nodes in the cluster.
Content indexing performance
Alfresco Repository
Recommendations:
- Increasing the number of concurrent consumers for the ActiveMQ queue
acs-repo-transform-request, can lead to missed content transformations. If you keep this value below10all the documents will be transformed.
Elasticsearch connector
Recommendations:
- Increase the timeout used to contact the Shared file store via HTTP, you set the value in
alfresco.sharedFileStore.timeout. This helps to avoid issues when the Shared File store response is slower than usual under a large load. - Increase the content retry delay used to retrieve content from the Shared File store, you set the value in
alfresco.content.event.retry.delay. This helps when you are uploading a large document into the system. - Select the correct configuration for the Shared File store content age scheduler. If you have disk space issues you can reduce it. You must consider you may find unexpected exceptions with a content reinsert request.
Searching performance
The Elasticsearch connector uses an out-of-the-box Elasticsearch server, for more see Tune for search speed.
Re-indexing
The Re-indexing app has been tested on reading replicas with a Postgres database. Tests have been performed on the local environment and AWS. To run database read replicas in AWS follow these guidelines AWS read replicas.
For using the read replica in the re-indexing phase, configure the reindexing component for targeting the correct read replica:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://<READ_REPLICA_ADDRESS>:<READ_REPLICA_PORT>/alfresco
Re-index using remote partitioning
It can take a large amount of time when re-indexing a large Alfresco Repository instance using a single re-index process. You can scale the re-index node vertically to improve performance, but this may also not enough. Using remote partitioning, and a Spring Batch feature, you can scale horizontally the Re-indexing service.
┌─────────────────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐
│ Manager │ │ Worker 1 │
│ │ Produce ┌────────────►│ ├───┐
│ │ partition │ │* Read partition│ │
│ * DB Schema Validation │ requests┌───┴──────┐ │* Index nodes │ │
│ ├──────────►│ ActiveMQ │ └──────┬─────────┘ │
│ * Partition creation │◀──────────┤ │ ◀───────────┘ │
│ │ └───┬──────┘ │
│ │ Consumes │ ▲ │
│ │ workers │ │ │
│ │ replies │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ ┌────────────────┐ │
└───────────┬─────────────┘ │ └───────────┤ Worker n │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ └────────────►│* Read partition│ │
│ │* Index nodes │ │
│ └────────┬───────┘ │
│ ┌────────────┐ │ │
│ │ Shared │◄──────────────────────────┘ │
└──────────►│ Database │ │
│ │◄──────────────────────────────────────┘
└────────────┘
This solution requires a manager node that executes verification steps, like database schema validation, and creates partitions and multiple worker nodes that index the partition. The manager sends partitions to the worker using ActiveMQ.
To use this feature you need to run a manager node and at least a worker node. To scale up the system you can increase the number of worker nodes by setting the property alfresco.reindex.partitioning.grid-size. The number of worker nodes usually equals the grid size, but if it is more a worker will consume multiple partitions.
The system will automatically select the partition strategy depending on the job name, currently there is:
- Partition by id range
- Partition by date range
Both strategies split the specified range into multiple ranges depending on the grid size.
Manager:
java -jar alfresco-elasticsearch-reindexing-3.1.0-app.jar \
--alfresco.reindex.jobName=reindexByIds \
--alfresco.reindex.partitioning.type=manager \
--alfresco.reindex.pagesize=100 \
--alfresco.reindex.batchSize=100 \
--alfresco.reindex.fromId=0 \
--alfresco.reindex.toId=10000 \
--spring.batch.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/alfresco \
--spring.batch.datasource.username=springBatchUser \
--spring.batch.datasource.password=****** \
--spring.batch.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver \
--spring.batch.drop.script=classpath:/org/springframework/batch/core/schema-drop-postgresql.sql \
--spring.batch.schema.script=classpath:/org/springframework/batch/core/schema-postgresql.sql
Worker:
java -jar alfresco-elasticsearch-reindexing-3.1.0-app.jar \
--alfresco.reindex.partitioning.type=worker \
--alfresco.reindex.pagesize=100 \
--alfresco.reindex.batchSize=100 \
--alfresco.reindex.concurrentProcessors=2 \
--spring.batch.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/alfresco \
--spring.batch.datasource.username=springBatchUser \
--spring.batch.datasource.password=****** \
--spring.batch.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver \
--spring.batch.drop.script=classpath:/org/springframework/batch/core/schema-drop-postgresql.sql \
--spring.batch.schema.script=classpath:/org/springframework/batch/core/schema-postgresql.sql
You don’t need to specify a job name for the worker because the configuration to use it is in the manager step context. This also means that you don’t need to restart a worker if the job name specified in the manager configuration changes.
The worker will not stop automatically because it is always up and running in order to wait for the new partition to index. The manager will automatically stop when all partitions have been indexed.
Batch Job Store DB
When using remote partitioning you are required to use a shared database that is accessible from all nodes. The database will contain the Batch job store. Spring batch will automatically create required tables, and those tables don’t contain sensitive data, so you can wipe them when required and you don’t need to back them up. It is recommended you use a unique database user to read the partition, and for managing the Spring batch. A list of supported databases can be retrieved, for more see Enum DatabaseType , and all available SQL initialization scripts are available, for more see spring-batch.
When using a different database you need to add to the Java classpath and to the right connection driver. The Re-indexing service is a Spring boot application which means you can’t add the JAR to the classpath, but instead you need to use a different command, for example:
java -cp alfresco-elasticsearch-reindexing-3.1.0-app.jar:mysql-connector-java-8.0.25.jar
-Dloader.main=org.alfresco.reindexing.ReindexingApp org.springframework.boot.loader.PropertiesLauncher
--alfresco.reindex.jobName=reindexByIds
--alfresco.reindex.partitioning.type=manager
--alfresco.reindex.fromId=0
--alfresco.reindex.toId=10000
--spring.batch.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/alfresco
--spring.batch.datasource.username=batchUser
--spring.datasource.username=batchUser
--spring.batch.datasource.password=*****
--spring.datasource.password=*****
--spring.batch.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
--spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
--spring.batch.drop.script=classpath:/org/springframework/batch/core/schema-drop-mysql.sql
--spring.batch.schema.script=classpath:/org/springframework/batch/core/schema-mysql.sql
Failures handling
If the manager** fails or a worker fails you can check which partitions were indexed in the log and launch them again by restarting the Re-indexing service.
Partition definition
The Re-indexing service creates partitions but only partitions the interval between the specified range, it is necessary to select the right range in order to avoid empty partitions. For instance, you can select the min and max values from the Alfresco database and then use those values in the configuration properties.
When re-indexing by ID range you can retrieve min and max values by executing the query below and using them for alfresco.reindex.fromId and alfresco.reindex.toId:
select min(id) as fromId, max(id) as toId from alf_node;
When re-indexing by date range you can retrieve min and max values by executing the query below and using them for alfresco.reindex.fromTime and alfresco.reindex.toTime:
select to_char(to_timestamp(min(commit_time_ms)/1000),'YYYYMMDDHHMI') as fromTime, to_char(to_timestamp(max(commit_time_ms)/1000),'YYYYMMDDHHMI') as toTime from alf_transaction;
It is easier to have unbalanced partitions when indexing by date range. Due to this it is recommended you use this strategy only when you are interested in indexing a specific date range. It is only recommended to perform a reindex by id range when you need to perform a full re-index.
Indexing only metadata
The Re-indexing application may be used to index only metadata. You can also exclude the content indexation from the process.
To apply this configuration, set the parameter alfresco.reindex.contentIndexingEnabled to false:
java -jar alfresco-elasticsearch-reindexing-3.1.0-app.jar \
--alfresco.reindex.contentIndexingEnabled=false
Indexing PATH property
By default, the re-indexing PATH property is disabled. To enable this feature, set the parameter alfresco.reindex.pathIndexingEnabled to true.
java -jar alfresco-elasticsearch-reindexing-3.1.0-app.jar \
--alfresco.reindex.pathIndexingEnabled=true
Enabling and disabling re-indexing features recommendations
By default the re-indexing application uses the following configuration:
alfresco.reindex.metadataIndexingEnabled=truealfresco.reindex.contentIndexingEnabled=truealfresco.reindex.pathIndexingEnabled=false
The re-indexing metadata process also indexes permissions associated with the document. This means when disabling metadata re-indexing, the content and path will not be updated for non-indexed documents. Only indexed documents will be updated with content and path.
The main use case to re-index only content or path is a fully metadata indexed repository that needs to update / complete the content or path.
Recommendations for large re-indexing processes
When indexing large repositories from scratch, the metadata indexing rate will be higher than the content indexing rate. This will increase the number of messages pending in the property acs-repo-transform-request from the ActiveMQ queue. However, since Basic ActiveMQ configuration is prepared to handle millions of Queue Messages per queue, this will not be an issue for the platform.
If you’re using a custom ActiveMQ configuration ensure ActiveMQ is not using a transient message store and is using paging cache.