Use this information to configure and deploy a custom AI model using Amazon Textract.
This guide takes you through the journey of configuring your Content Services instance to enrich the content with custom metadata detected with powerful state of the art AI algorithms.
Multiple custom entity model can be configured and used in Content Services simultaneously, on either the same or different folders, using a flexible configuration.
Follow the remaining sections to start setting up your custom Textract models.
Step 1: Define custom Textract models
There are two parts to creating a Custom Metadata Extraction model:
- Configuring custom mapping for Textract metadata extraction from forms (as key-value pairs)
- (Optional) Mapping basic OCR detected text lines into a multi-valued text field to enable viewing and searching (using the out-of-box
ai:textLinesaspect)
Custom mapping
As a developer or administrator, you can define a custom AI content model to enable mapping of extracted text values into Content Services content model properties (or metadata). You can define one or more aspects, each with one or more properties, where each aspect can extend a new “out-of-the-box” parent aspect (ai:textract). Note that this is similar to the Comprehend parent aspect, ai:features.
- The properties may be single-valued or multi-valued.
- Typically, extracted text values map to properties of data type
d:text. - Check boxes typically map to
d:boolean.
However, in theory, the property may be of any data type to which the extracted value can be mapped without a constraint violation.
You’ll need to define the custom Textract metadata configuration in JSON format. This should allow one or more specific key-value pairs to map to the Content Services content model properties. Different aspects may be configured for different document types. The configuration can be statically bootstrapped by the repository on startup.
Note: Textract tables and cells are currently out-of-scope.
Form extraction (key-value pairs)
Here’s an example of the metadata extracted from a form:
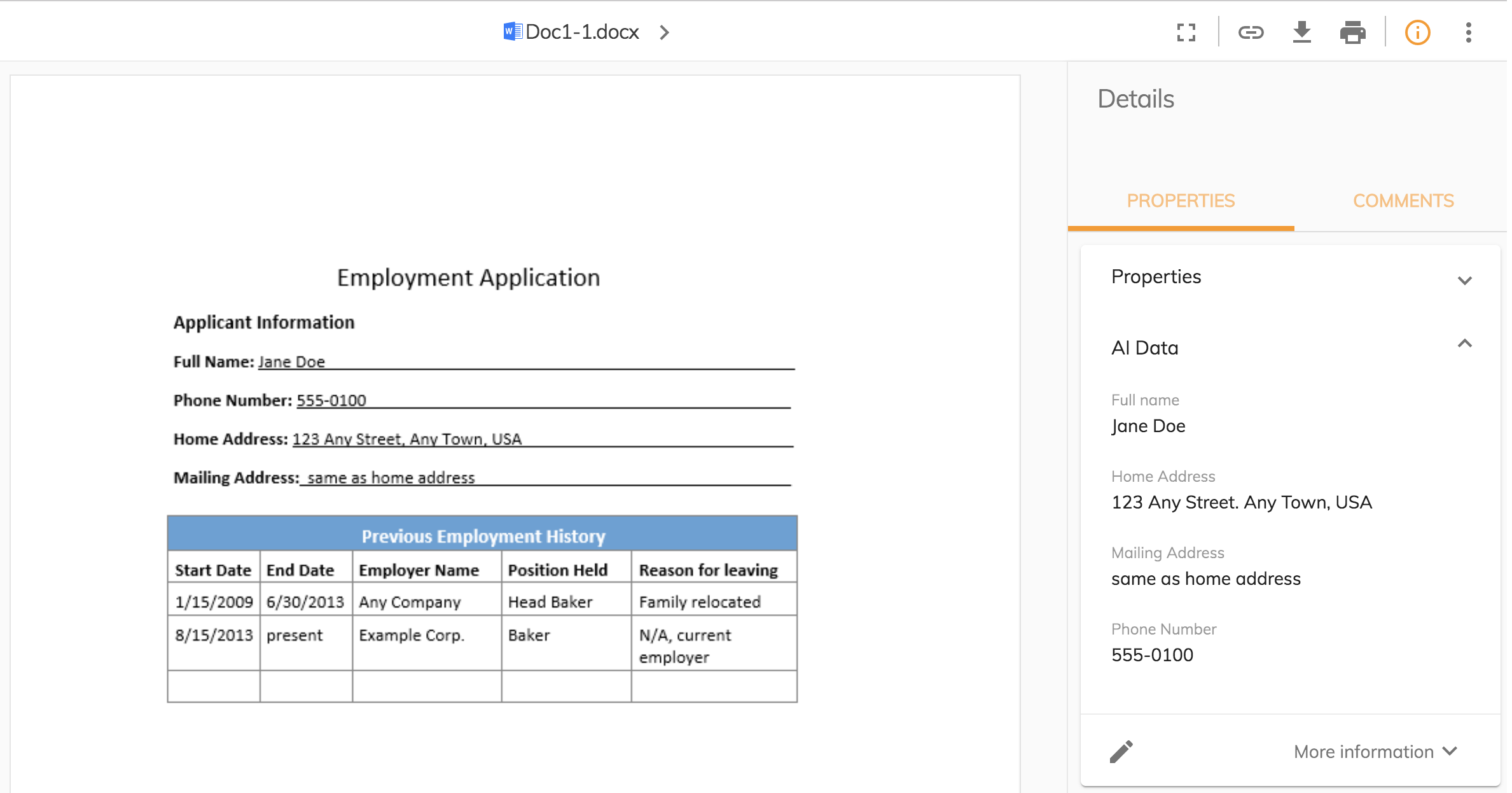
Key matching
Multiple types of key matching are supported:
- default matching:
- ignores case
- ignores non-alphanumeric prefixes and suffixes
- ignores whitespace
Note: The default matching would have to process not just the keys received in the Textract JSON response, but also the keys defined in the property mapping configuration files.
- exact matching
- regular expression (regex) matching
The key matching type can be defined for each key in the property mapping configuration file. If omitted, the default matching is used.
Multiple keys mapped to one property
Key matching implies a number of different keys may map to the same property. Hence, you may define exact match keys that map to the same property.
When the same key matches multiple times or a number of different matching keys map to the same property then:
- for a multi-value property - each unique value is stored
- for a single-value property - the most confident match of a key-value-set is stored, along with the INFO log messages that some values were skipped/ignored.
One key mapped to multiple properties
Due to the supported matching types, keys may match and overlap such that they map to different properties. Similarly, we allow the mapping of one key to multiple properties (by multiple aspects).
When the same matching key maps two different properties, we map to both properties, and log an INFO message with the context.
Confidence
The minimum confidence level is checked when mapping each matching element (key-value pair). This uses a new global (system-wide) property:
ai.transformation.aiTextract.keyValueSet.minConfidence
This property has a default: 0.7 (i.e. 70%) unless overridden for a specific key/value mapping.
You can add an optional confidence field for each key in the property mapping configuration file to override the global configuration. See example in Custom AI property mapping.
Custom aspects
An aspect can contain multiple properties (multiple keys). Different aspects can be defined depending on the documents that need to be processed. Their keys might overlap.
Log messages
- If a mapped key value fails to convert the extracted text string to a different target data type (for example, due to constraint violation) it’ll be skipped with a one-line INFO log message (including context, for example, nodeId, property name and value).
- If the same key matches multiple times, or multiple different matching keys map to the same single-value property then we store the “most confident match of a key-value-set”, and specify in an INFO log message that some values were skipped/ignored.
- If the same matching key maps two different properties, we map to both properties and state the behavior in an INFO log message.
Check boxes
Check boxes detected within forms (Textract selectables as key-value pairs) are supported. In this case, you can choose to map to d:boolean (i.e. whether selected or not) or d:text. For d:text, the selected status value is stored as returned by Textract, i.e. SELECTED or NOT_SELECTED.
Here’s an example of the metadata extracted from a form that shows both options mixed together in a single aspect:

Raw text extraction
There’s an out-of-box AI Text Lines aspect (with a d:text property type) that an end-user can optionally use when configuring a rule. This enables a non-custom way to extract the Textract “raw text”, so that OCR’d text (above the minimum confidence for lines) can be viewed as metadata, as well as being indexed and searchable.
Out-of-the-box, the raw text lines are stored in a multi-valued text property (which appear comma-separated in Alfresco Digital Workspace).
The ai-content-model.xml contains an aspect for the raw text. This is included by default in the Intelligence Services AMP:
<aspect name="ai:textLines">
<title>AI Text Lines</title>
<parent>ai:textract</parent>
<properties>
<property name="schema:textLines">
<title>Text</title>
<type>d:text</type>
<multiple>true</multiple>
<index enabled="true">
<tokenised>both</tokenised>
<facetable>true</facetable>
</index>
</property>
</properties>
</aspect>
Step 2: Deploy and configure a custom model
Use this information to deploy and configure a custom model for Intelligence Services.
Note that the implementation follows the same process for custom recognition or classification model types, but differs slightly for custom metadata extraction.
Before you can use a custom model with Intelligence Services, you’ll need to define a new rendition in configuration files for the repository, Alfresco Share, and Alfresco Digital Workspace.
The process requires the configuration of a number of files that must be mounted in the Docker containers:
| Configuration file | Used by custom model / AWS service | |
|---|---|---|
| Repository | custom-ai-content-model-context.xml | Comprehend, Textract |
| customAIContentModel.xml | Comprehend, Textract | |
| custom-ai-renditions-definitions.json | Comprehend | |
| customAIPropertyMapping.json | Comprehend, Textract | |
| Share | share-config-custom.xml | Comprehend, Textract |
| bootstrap-custom-labels.properties | Comprehend | |
| share-custom-slingshot-application-context.xml | Comprehend, Textract | |
| Digital Workspace | ai-view.extension.json | Comprehend, Textract |
These files are described in more detail in the remainder of this page.
Step 3: Configure the repository
Use this information to configure the repository files needed for a custom Textract model.
The following files must be mounted in the repository Docker container.
Custom AI content model context
File name: custom-ai-content-model-context.xml
Mount location and example:
./custom-ai-content-model-context.xml:/usr/local/tomcat/shared/classes/alfresco/extension/custom-ai-content-model-context.xml
Content:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<!-- Registration of new models -->
<bean id="org.alfresco.acme.dictionaryBootstrap" parent="dictionaryModelBootstrap" depends-on="org.alfresco.ai.dictionaryBootstrap">
<property name="models">
<list>
<value>alfresco/extension/customAIContentModel.xml</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
Custom AI content model
File name: customAIContentModel.xml
Mount location and example:
./customAIContentModel.xml:/usr/local/tomcat/shared/classes/alfresco/extension/customAIContentModel.xml
Content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<model name="acme:contentModel" xmlns="http://www.alfresco.org/model/dictionary/1.0">
<description>Custom Content Model for Artificial Intelligence extension</description>
<version>1.0</version>
<imports>
<import uri="http://www.alfresco.org/model/content/1.0" prefix="cm" />
<import uri="http://www.alfresco.org/model/dictionary/1.0" prefix="d" />
<import uri="http://www.alfresco.org/model/site/1.0" prefix="st" />
<import uri="http://www.alfresco.org/model/system/1.0" prefix="sys" />
<import uri="http://www.alfresco.org/model/ai/1.0" prefix="ai"/>
</imports>
<namespaces>
<namespace uri="http://acme.org" prefix="acme" />
</namespaces>
<aspects>
<aspect name="acme:applicantInfo">
<title>Applicant Info</title>
<parent>ai:textract</parent>
<properties>
<property name="acme:addressHome">
<title>Address (Home)</title>
<type>d:text</type>
<index enabled="true" />
</property>
<property name="acme:nameFull">
<title>Name (Full)</title>
<type>d:text</type>
<index enabled="true" />
</property>
<property name="acme:telephone">
<title>Telephone</title>
<type>d:text</type>
<index enabled="true" />
</property>
[...]
</properties>
</aspect>
<aspect name="acme:w9form">
<title>W-9</title>
<parent>ai:textract</parent>
<properties>
[...]
</properties>
</aspect>
</aspects>
</model>
Custom AI property mapping
File name: customAIPropertyMapping.json
Mount location and example:
./customAIPropertyMapping.json:/usr/local/tomcat/customAIPropertyMapping.json
Content:
{
"keyValueMapping":[
{
"aiTextract":[
{
"key":"Mailing Address:",
"aspect":"acme:applicantInfo",
"property":"acme:addressHome",
"keyMatch": "EXACT"
},
{
"key":"Full Name",
"aspect":"acme:applicantInfo",
"property":"acme:nameFull",
"confidence": "0.5"
},
{
"key":"telephone number:",
"aspect":"acme:applicantInfo",
"property":"acme:telephone"
},
[...]
]
}
]
}
In the above JSON snippet:
- The property mapping configuration is loaded and validated at application startup.
- If there’s a mismatch between the aspect and the property, or if one or the other doesn’t exist, a
WARNmessage is logged, and the pairing is ignored (i.e. that particular pair is ignored, not the entire configuration). - This example uses an
EXACTkey matching for theMailing Addressfield. Other options include regular expressions, with a fallback to the default matching ifkeyMatchisn’t defined. See Form extraction (key-value pairs) for more.
Step 4: Configure Share and Digital Workspace
Use this information to configure the files needed by Share and Digital Workspace for a custom Textract model.
Share
The following files must be mounted in the Share Docker container.
1. Custom AI labels
File name: share-config-custom.xml
Mount location and example:
./share-config-custom.xml:/usr/local/tomcat/shared/classes/alfresco/web-extension/share-config-custom-dev.xml
Content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<alfresco-config>
<config evaluator="string-compare" condition="DocumentLibrary">
<!-- Aspects that a user can see -->
<aspects>
<visible>
<aspect name="acme:applicantInfo"/>
<aspect name="acme:w9form"/>
</visible>
</aspects>
</config>
</alfresco-config>
Note: The
ai:textLinesaspect is pre-configured in the Share AMP, so it doesn’t need to be added to the custom configuration.
2. Custom AI aspect configuration
File name: bootstrap-custom-labels.properties
Mount location and example:
./bootstrap-custom-labels.properties:/usr/local/tomcat/shared/classes/alfresco/web-extension/messages/bootstrap-custom-labels.properties
Content:
aspect.acme_applicantInfo=Applicant Info
aspect.acme_w9form=W-9
3. Custom AI labels context
File name: share-custom-slingshot-application-context.xml
Mount location and example:
./share-custom-slingshot-application-context.xml:/usr/local/tomcat/shared/classes/alfresco/web-extension/custom-slingshot-application-context.xml
Content:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="org.alfresco.acme.alfresco-ai-share.resources" class="org.springframework.extensions.surf.util.ResourceBundleBootstrapComponent">
<property name="resourceBundles">
<list>
<value>alfresco/web-extension/messages/bootstrap-custom-labels</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
Digital Workspace
The Digital Workspace configuration for custom AI requires modification of an existing configuration file (ai-view.extension.json). The JSON file is included in the Intelligence Services distribution zip. This is unlike the repository and Share configuration, where only new files are created and mounted in the containers.
App extension
File name: ai-view.extension.json
Mount location and example:
./ai-view.extension.json:/usr/share/nginx/html/assets/plugins/ai-view.extension.json
Content:
[...]
"content-metadata-presets": [
{
"id": "app.content.metadata.custom",
"custom": [
{
"id": "ai.metadata.features",
"title": "AI Data",
"items": [
{
"id": "acme:applicantInfo",
"aspect": "acme:applicantInfo",
"properties": "*"
},
{
"id": "acme:w9form",
"aspect": "acme:w9form",
"properties": "*"
},
[...]
]
}
],
[...]
}
]
The above snippet adds the aspects in the earlier Custom AI content model configuration (for Textract) to the existing "ai.metadata.features" list of items in the ai-view.extension.json file.
For more details on extending the features of Digital Workspace, see the Alfresco Content Application documentation: Extending.