Content models describe how data should be stored in the repository and the metadata that can be associated to the content and folders within that model.
Each model is identified by a unique namespace, prefix and name, and made up of custom types, aspects, properties and constraints.
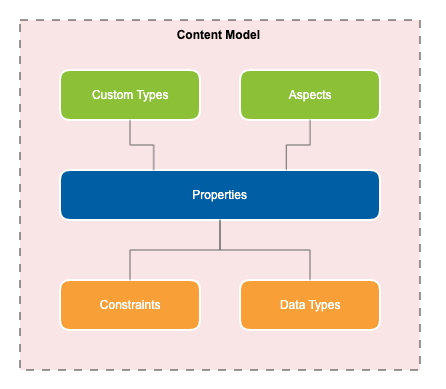
Properties
The properties of a content model are:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Content model name | Required. The name of the content model. Must be in lowercase and between 1 and 26 characters in length. Alphanumeric characters and hyphens are allowed, however the name must begin with a letter and end alphanumerically, for example finance. |
| Namespace | Required. A namespace unique within the repository for the content model to sit under. This ensures that all custom types, aspects and properties are also unique within the repository. The default value will append the Name of the model, for example http://finance.com/model/finance. |
| Prefix | Required. An abbreviation of the namespace of a content model to refer to types and aspects without needing to use the full namespace. The default value will be the Name of the model, for example finance. |
| Creator | Optional. The author of the model. The default value is the currently signed in user, for example modeler. |
| Content model description | Optional. A free text description of what the content model is for, for example A content model for recording financial accounts records. |
Create a content model
Content models can be global in scope, so they are available to import into multiple projects or they can be created at an individual project level.
Create a global content model
To create a global content model:
-
Sign into the Modeling Application and click on Content Models.
-
Click the NEW dropdown.
-
Select Content Model and enter a name and optional description.
To use a global content model within a specific project:
-
Sign into the Modeling Application and open a project.
-
Click the NEW dropdown.
-
Select Import > Content Model and choose the model to import.
Create a content model in a project
To create a content model in a project:
-
Sign into the Modeling Application and open a project.
-
Click the NEW dropdown.
-
Select how to create the content model:
-
Create > Content Model creates a new, empty form.
-
Upload > Content Model allows for uploading an existing content model
.xmlfile into the Modeling Application.
Alternatively use the + or Upload buttons next to Content Models in the left-hand menu.
-
-
Enter a name and optional description.
Content model modeling
Content models are created within a project and are exclusive to that project unless the content model scope is changed to global. Once a content model is global it will appear at the same level as projects in the modeling application and can be imported into other projects.
Use the Turn global option under actions when a content model is selected to change the scope to global.
Note: It is not possible to change the scope back to a single project once the Turn global option has been used. The content model will need to be removed from the project and either recreated, or reimported.
Custom types
Custom types set the properties and relationships that a file of that type can support. Custom types can inherit the properties of a parent type. Content and Folder are two example types that are already defined in Alfresco Content Services.
The properties of a custom type are:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Required. The name of the custom type. Custom type names can only contain alphanumeric characters, hyphens and underscores, for example supplier-invoice. |
| Parent type | Required. A parent type for the custom type. All properties and aspects assigned to the parent are inherited by the child, for example cm:content. |
| Title | Optional. A display label for the custom type that will be displayed to users, for example Supplier Invoice. |
| Description | Optional. A free text description of what the custom type is for, for example An invoice received from a supplier. |
Custom types are stored as JSON, for example:
{
"parentName": "cm:content",
"name": "supplier-invoice",
"prefixedName": "finance:supplier-invoice",
"description": "An invoice received from a supplier.",
"title": "Supplier Invoice",
"properties": []
}
Aspects
Aspects are a collection of properties that can be used to describe data and behavior. A file must be of one type, however it can have multiple aspects attached to it. Classifiable and Versionable are two example aspects that are already defined in Alfresco Content Services.
The properties of an aspect are:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Required. The name of the custom aspect. Custom aspect names can only contain alphanumeric characters, hyphens and underscores, for example isArchivable. |
| Title | Optional. A display label for the custom aspect that will be displayed to users, for example Archivable. |
| Description | Optional. A free text description of what the custom aspect is for, for example The status of the document for archiving purposes. |
Aspects are stored as JSON, for example:
{
"name": "isArchivable",
"prefixedName": "finance:isArchivable",
"description": "The status of the document for archiving purposes.",
"title": "Archivable",
"properties": []
}
Properties
Properties are the metadata that describe content. Author is an example property that is already defined in Alfresco Content Services used for specifying who wrote the content.
Properties can be assigned to a custom type or an aspect. Select which type or aspect to create the property under before creating it.
The properties of properties are:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Required. The name of the property. Property names can only contain alphanumeric characters, hyphens and underscores, for example datePaid. |
| Title | Optional. A display label for the property that will be displayed to users, for example Date Paid. |
| Description | Optional. A free text description of what the property is for. For example The date the invoice was paid. |
| Data type | Optional. The data type of the property. See the following table for a list of data types, for example d:date. |
| Mandatory | Optional. Set whether the property is mandatory, for example false. |
| Multiple | Optional. Set whether the property can contain multiple values, for example false. |
| Default value | Optional. Set a default value for the property. |
| Constraint | Optional. Set a constraint on the values that can be entered for the property, for example Regular expression. |
| Indexing | Optional. Set whether the property can be searched on and how it is searchable, for example Free text. |
The options for data types of properties are:
| Data type | Description |
|---|---|
| d:text | A sequence of characters |
| d:mltext | A multilingual sequence of characters containing localized representations |
| d:int | A positive whole number |
| d:float | A float value |
| d:double | A double value generally used for decimal values |
| d:date | A specific date in the format DD-MM-YYYY |
| d:datetime | A specific date and time |
| d:boolean | A value of either true or false |
The options for constraints of properties are:
| Constraint type | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular expression | Set a regular expression that values must match to be valid for example, a regular expression that matches four letters followed by four digits would be: /^[A-Za-z]{4}\d{4}$/ |
| Minimum / maximum length | Set the minimum and maximum number of characters a value for the property can be, for example 0 and 10. |
| Minimum / maximum value | Set the minimum and maximum values for properties, for example 5. |
| List of values | Set a list of predefined values the property must be chosen from, for example payable,non-payable,unknown. |
| Java class | Set the fully qualified Java class to use for restricting the values of the property. |
The index options of properties are:
| Search type | Description |
|---|---|
| None | The property is not searchable. |
| Free text | Property is searchable but the values will not be available in the search result filters. |
| List of values - whole match | This option enables you to filter on a property in the search results while searching for the whole term. |
| List of values - partial match | This option enables you to filter on a property in the search results while searching the property using wildcard characters. |
| Pattern - unique matches | This option enables you to use unique identifiers which are searched on the basis of the full value of the property. The property itself will not be shown as a filter in the search results. |
| Pattern - many matches | This option enables you to use identifiers which could be searched on the basis of the full value or via the wild card characters. The property itself will not be shown as a filter in the search results. |
Properties are stored as JSON, for example:
{
"name": "datePaid",
"prefixedName": "finance:datePaid",
"title": "Date Paid",
"description": "The date the invoice was paid.",
"dataType": "d:date",
"facetable": "UNSET",
"indexTokenisationMode": "TRUE",
"multiValued": false,
"mandatoryEnforced": false,
"mandatory": false,
"indexed": true
}
Actions
The actions that can be run against a content model are:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Download content model | Download the XML for the content model. |
| Validate | Run validation against the content model. Any errors can be seen in the log history at the bottom of the Modeling Application and are flagged in a pop-up box. |
| Save | Save any changes made to the content model. |
| Turn global | Changes the content model to have a global scope, so it can be imported into multiple projects. This action is only available if the content model is not already of global scope. |
| Remove from project | Removes the content model from the project. This action is only available if the content model is already set to global scope. |
| Delete | Delete the content model. |