Scripts are used to execute a script as part of a process. Process variables can be passed to the script and the results of a script can be sent back to a process instance as process variables. Any JavaScript that is created by the modeling application has the same permissions assigned to it as the logged in user. This is helpful because it allows the logged in user to test their own scripts with their own files.
Script design uses the functionality of the Monaco Editor and uses the GraalVM JavaScript Engine for execution.
Scripts are added to a process definition using a script task.
Properties
The basic properties of a script are:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Script name | Required. The name of the script. Must be in lowercase and between 1 and 26 characters in length. Alphanumeric characters and hyphens are allowed, however the name must begin with a letter and end alphanumerically, for example order-script |
| Language | Required. The development language the script is written in, for example Javascript. |
| Script description | Optional. A description of what the script should be used for, for example Returns the prefixed order number. |
Create a script
To create a script:
-
Sign into the Modeling Application and open a project.
-
Click the NEW dropdown.
-
Select how to create the script:
-
Create > Script creates a new, empty script.
-
Upload > Script allows for uploading an existing script
.binfile into the Modeling Application.
Alternatively use the + or Upload buttons next to Scripts in the left-hand menu.
-
-
Enter a name and optional description.
Script modeling
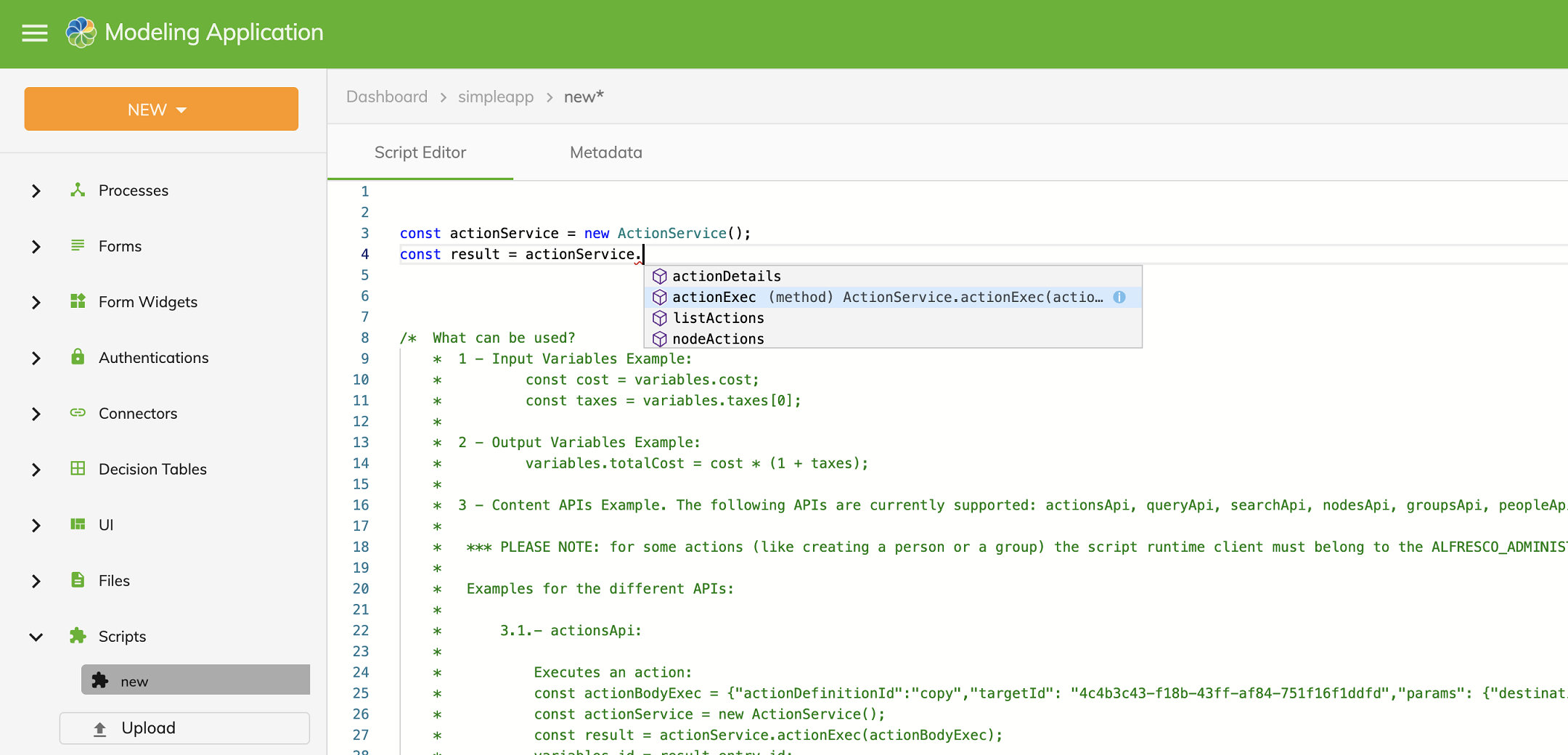
The Modeling Application contains two tabs for creating and managing scripts.
The Script Editor is the GUI for modeling scripts by typing in the declared language. The editor has autocomplete functionality for APIs and script variables. The Metadata contains the properties related to the script.
Simulation
Once a script has been written, it can be simulated by entering potential inputs and viewing their output.
In the UI click the Simulate button after entering the input values to simulate. The results will be populated in the outputs section.
Variables
There are two types of variables associated with a script. Script variables are stored as JSON and are used to pass values between a process and a script. Declared variables are used within the script body itself.
Script variables
Script variables can be used to pass and receive values from process variables.
The properties for a script variable are:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| name | A unique name that can contain alphanumeric characters and underscores but must begin with a letter, for example var_3 |
| type | A data type selected from a dropdown. See the following table for a list of data types, for example String |
| required | Sets whether the script variable must contain a value when the task is started, for example false |
| value | An optional default value for the script variable, for example ice-cream |
The data types that a script variable can be set as are:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| String | A sequence of characters, for example #Mint-Ice-Cream-4! |
| Integer | A positive whole number, for example 642 |
| Boolean | A value of either true or false |
| Date | A specific date in the format YYYY-MM-DD, for example 2020-04-22 |
| Datetime | A specific date and time in the format YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss, for example 2020-09-10 22:30:00 |
| File | A file uploaded into a process definition or as part of a process instance or task |
| JSON | A JSON object, for example {"flavor" : "caramel"} |
| Folder | A folder object described as JSON, for example "name": "mint-folder" |
| Array | A comma separated list of entries, for example mint, strawberry, vanilla that will be formatted to ["mint","strawberry","vanilla"] |
Declared variables
Declared variables are used within the script itself and can be set to the value of a script variable by using the prefix variables. to reference the script variable. An input variable will set a declared variable to the value of a script variable when the script is executed.
For example, in a process the script variables cost and orders will have their values set from process variables. The declared variables costOfItem and numberOfOrders can then be set to these values using the following:
let costOfItem = variables.cost;
let numberOfOrders = variables.orders;
The value of the script variable totalCost will then be set after the script has executed by using the following:
variables.totalCost = costOfItem * numberOfOrders;
The value of the script variable totalCost can finally be sent back to the process by mapping it to a process variable.
Process scripts
Scripts can be used to start a process instance by building a payload.
For example, use the process definition ID and set the process variables using:
let startProcessInstanceCmd = processPayloadBuilder.start()
.withProcessDefinitionKey("Process_GyW7Ekkw")
.withVariable("orderNumber": variables.orderNumber)
.withVariable("quantity": variables.quantity)
.build();
commandProducer.send(startProcessInstanceCmd);
Content APIs
The following content APIs are supported:
ActionServiceGroupServiceNodeServicePeopleServiceQueryServiceSearchServiceSiteServiceTagService
Note: The API scripts can be tested in the simulator on the scripts window.
You can create the object by accessing the API which then allows you to make use of all its methods.
For example:
const nodeBodyCreate = { name: variables.name, nodeType: "cm:folder" };
const nodeService = new NodeService();
nodeService.createNode(variables.parentNodeId, nodeBodyCreate);
Runtime APIs
The following APIs are supported:
ProcessInstanceAdminControllerImplApiProcessInstanceControllerImplApiProcessInstanceTasksControllerImplApiProcessInstanceVariableAdminControllerImplApiProcessInstanceVariableControllerImplTaskAdminControllerImplApiTaskControllerImplApiTaskVariableAdminControllerImplApiTaskVariableControllerImplApi
Using the following names you can perform all the actions related to the APIs mentioned above:
RuntimeProcessInstanceAdminService: APA Runtime Process Instance Admin REST API (it includesProcessInstanceAdminControllerImplApi, andProcessInstanceVariableAdminControllerImplApi)RuntimeProcessInstanceService: APA Runtime Process Instance REST API (it includesProcessInstanceControllerImplApi,ProcessInstanceTasksControllerImplApi, andProcessInstanceVariableControllerImpl)RuntimeTaskAdminService: APA Runtime Task Admin API (it includesTaskControllerImplApi, andTaskVariableAdminControllerImplApi)RuntimeTaskService: APA Runtime Task API (it includesTaskControllerImplApi, andTaskVariableControllerImplApi)
For example:
const startProcessPayload = { businessKey: variables.businessKey, payloadType: 'StartProcessPayload', processDefinitionKey: variables.processKey, variables: { fileArray: variables.fileArray } };
const runtimeProcessInstanceService = new RuntimeProcessInstanceService();
runtimeProcessInstanceService.startProcess(startProcessPayload);
Query APIs
The following APIs are currently supported:
ProcessInstanceAdminControllerApiProcessInstanceControllerApiProcessInstanceDeleteControllerApiProcessInstanceDiagramAdminControllerApiProcessInstanceDiagramControllerApiProcessInstanceServiceTasksAdminControllerApiProcessInstanceTasksControllerApiProcessInstanceVariableAdminControllerApiProcessInstanceVariableControllerApiTaskAdminControllerApiTaskControllerApiTaskVariableAdminControllerApiTaskVariableControllerApi
You can use the following names to perform all the actions related to the APIs indicated above:
QueryProcessInstanceAdminService: APA Query Process Instance Admin REST API (it includesProcessInstanceAdminControllerApi,ProcessInstanceDiagramAdminControllerApi,ProcessInstanceServiceTasksAdminControllerApi, andProcessInstanceVariableAdminControllerApi)QueryProcessInstanceService: APA Query Process Instance REST API (it includesProcessInstanceControllerApi,ProcessInstanceDeleteControllerApi,ProcessInstanceDiagramControllerApi,ProcessInstanceTasksControllerApi, andProcessInstanceVariableControllerApi)QueryTaskAdminService: APA Query Task Admin API (it includesTaskAdminControllerApi, andTaskVariableAdminControllerApi)QueryTaskService: APA Query Task API (it includesTaskControllerApi, andTaskVariableControllerApi)
For example:
const queryProcessInstanceAdminService = new QueryProcessInstanceAdminService();
queryProcessInstanceAdminService.findById('idProcess');
Form API
The following API is currently supported:
FormApi
You can use the following name to perform all the actions related to the API indicated above:
FormService: APA Form API (it includesFormApi)
For example:
const formId = variables.formId;
const formService = new FormService();
const form = formService.getFormDefinition(formId);
Actions
The actions that can be run against a script are:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Download script | Download the bin file for the script. |
| Validate | Run validation against the script. Any errors can be seen in the log history at the bottom of the Modeling Application and are flagged in a pop-up box. |
| Save | Save any changes made to the script. |
| Delete | Delete the script. |